Specifications
Surface Treatments
Certifications
- ISO 9001 - 2015 Certified
- PED 2014/68/EC
- NACE MR0175/ISO 15156-2
- NORSOK M-650
- DFAR
- MERKBLATT AD 2000 W2/W7/W10
Incoloy® Alloy A286 is iron-nickel-chromium based austenitic iron based material that consist of molybdenum and titanium as an addition. Cres A286 alloy is known for its good strength and oxidation resistance especially at temperatures up to 1300°F (700°C). A286 is an age-hardenable iron-nickel-chromium alloy that is one of the most popular and widely used of high temperature alloys. It maintains good strength with oxidation resistance at temperatures of up to 1300°F. A286 is used in various components, such as aircraft and industrial gas turbines due to is high strength and superior fabrication. A286 is also very popular in offshore oil and gas industry where high levels of heat and stress are a factor.
Incoloy Alloy A286 (® Special Metals)
Pyromet Alloy A286 (® Carpenter Technology)
ATI A286 (™ Allegheny Technologies)
TURBALOY® 286VM(United States Welding Corporation)
| Elements | DIN EN 10269 | VdTÜV Werkstoffblatt 435 |
ASTM A453 Grade 660 A/B/C/D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C), max. | 0.03 - 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Manganese (Mn), max. | 1.00 - 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorous (P), max. | 0.025 | 0.030 | 0.040 |
| Sulphur (S), max. | 0.015 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si), max. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 13.5 - 16.0 | 13.5 - 16.0 | 13.5 - 16.0 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 24.0 - 27.0 | 24.0 - 27.0 | 24.0 - 27.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.00 - 1.50 | 1.00 - 1.50 | 1.00 - 1.50 |
| Titanium (Ti) | 1.90 - 2.30 | 1.9 - 2.3 | 1.90 - 2.35 |
| Aluminium (Al), max. | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.10 - 0.50 | 0.10 - 0.50 | 0.10 - 0.50 |
| Boron (B) | 0.003 - 0.010 | 0.003 - 0.010 | 0.001 - 0.010 |
Density: 0.287 lb/in3, (7.94 g/cm3)
Modulus of Elasticity (E): At 70°F (20°C): 28.8 x 103 ksi (199 GPa)
Modulus of Rigidity (G): At 70°F (20°C): 11.2 x 103 ksi (77.0 GPa)
Coefficient of Expansion: 9.47 µin/in.-°F (70°F to 600°F) | 17.0 µm/m-°C (20°C to 300°C)
Electrical Resistivity: 35.8 µΩ.in, (91 µΩ.cm)
Thermal Conductivity: 88 Btu-in/ft2hr-°F, (12.7 W/m-K)
| Solution Annealed / Precipitation Hardened |
Bar | Forged Bar / Forgings | Bar |
|---|---|---|---|
| D ≤ 160 mm | D ≤ 300 mm | Typical | |
| Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) | 900 - 1150 | 900 - 1200 | ≥ 895 |
| Yield Stress Rp 0.2 (MPa) | ≥ 600 | ≥ 600 | ≥ 585 |
| Elongation L=4d (%) | l ≥ 15 | l ≥ 16, q ≥ 14 | ≥ 15 |
| Reduction Z (%) | ≥ 18 | ||
| Charpy Notch Impact Av (J) | ≥ 50 | l ≥ 56, q/t ≥ 32 | |
| Hardness (BHN) | 248 - 341 |
A286 alloy is designed to withstand elevated temperature strength. Typical Creep Strength and stress rupture strengths of material aged at 1325°F (718°C) are shown below. Two Different type solution treatments are used to achieve respective stress rupture properties viz:
For high stress rupture strength Solution treat at 1800°F (982°C) for 1 hour, rapid cool, age at 1325°F (718°C) for 16 hours and air cool.
For high room temperature tensile strength and stress rupture ductility, Solution treat at 1650°F (899°C) for 2 hour, rapid cool, age at 1325°F (718°C) for 16 hours and air cool.
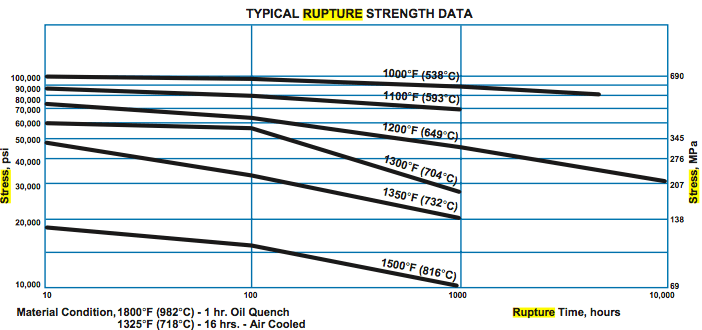
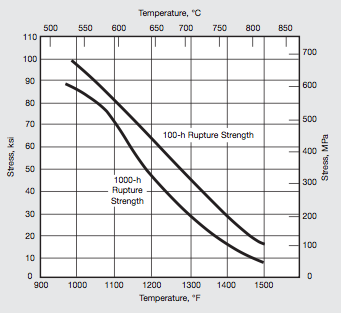
| Degrees Fahrenheit | Degrees Celcius | 100 Hours | % elongation in 3D | 1000 Hours | %,elongation in 4D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ksi | Mpa | Ksi | Mpa | ||||
| 1000 °F | 538 °C | 99 Ksi | 683 Mpa | 3% | 88 Ksi | 607 Mpa | 3% |
| 1100 °F | 593 °C | 81.5 Ksi | 562 Mpa | 3% | 71.5 Ksi | 493 Mpa | 3% |
| 1200 °F | 639 °C | 61 Ksi | 421 Mpa | 5% | 46 Ksi | 317 Mpa | 8.5 % |
| 1300 °F | 704 °C | 44.5 Ksi | 307 Mpa | 12 % | 29 Ksi | 200 Mpa | 30 % |
| 1350 °F | 732 °C | 35 Ksi | 41 Mpa | 29 % | 21 Ksi | 145 Mpa | 35 % |
| 1500 °F | 816 °C | 13 Ksi | 90 Mpa | 55 % | 7.7 Ksi | 53 Mpa | - |
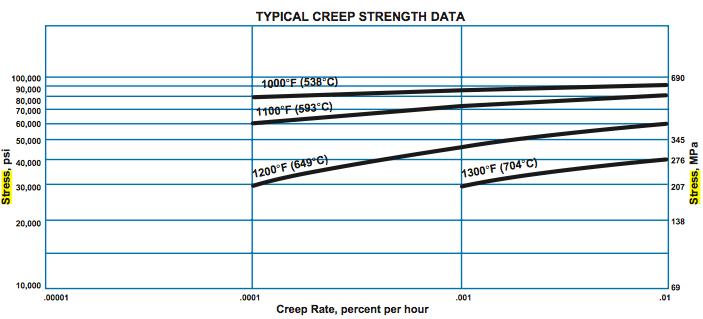
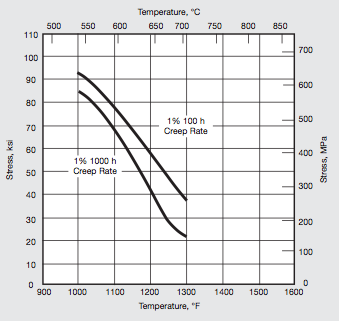
A286 Alloy has corrosion resistance similar to austenitic stainless steels in many environments. Cres-A286 has superior corrosion resistance to nickel-base alloys when exposed to sulfur contaminated atmospheres at elevated temperatures.The corrosion resistance of this alloy is excellent up to 1300 °F(704 °C) against many atmospheres encountered in jet engine service. Up to 1800 °F(982 °C), the oxidation resistance of alloy A286 is equivalent to that of 310 Stainless Steel.
Cres A286 has excellent oxidation resistance up to 1,800°F (982°C). High temperature sustainability and high tensile strength is the key factor for superior Oxidation resistance property of Alloy A286.
Due to the high strength and reliable fabrication characteristics of Cres A286, It is widely used in manufacturing and fabrication of various components used in turbines mainly in gas industry and aircraft applications . It is also used for fastener applications in automotive engine and manifold components subject to high levels of heat and stress and in the offshore oil and gas industry.
Alloy A286 steel has similar forging properties as compared to austenitic stainless steels. Initial forging is usually performed from 2,000- 2,150°F (1,093 - 1,177°C) with finishing temperatures from 1,650-1,700 F (899 - 927°C).15 - 20 percent minimum reduction should be combined with a low finishing temperature to produce a fine, uniform grain size. The formability of Alloy A286 alloy in the solution annealed condition is similar to Type 310 stainless steel.
ATI A286TM alloy in the solution annealed condition is similar to ATI 310 stainless steel.
Being and austenitic Stainless Steel with 24 percent nickel content, Alloy A286 is an iron-base alloy which is easier to machine as compared to nickel-based precipitation-hardening steels.
The machinability of Alloy A286 is similar to that of the austenitic stainless steels specifically Stainless steel type 310. Cres Alloy A286 is usually machined in the full aged or partially aged condition.
Carbide insert tools are commonly used for machining Alloy 286.
Alloy A286 steel can be welded in the solution annealed condition in thin sections, and in large sections under conditions of low restraint. However, the alloy is subject to hot cracking, particularly in the aged condition. Sound welds can be produced by inert gas shielded arc, spot, resistance seam, ash butt, and electron beam welding techniques.